
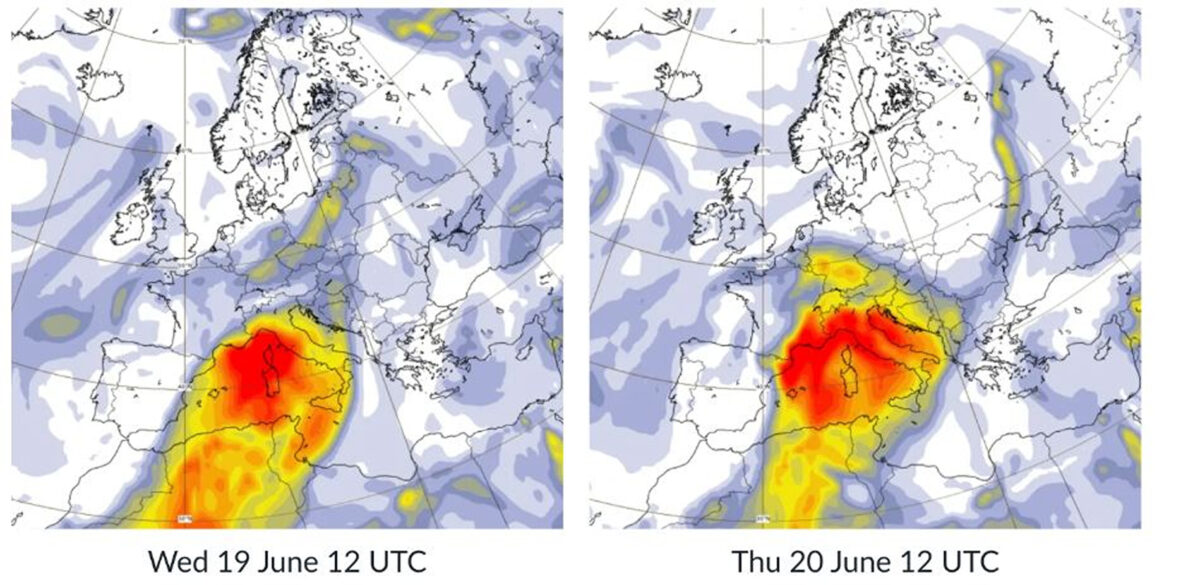
Sahara dust has entered the atmosphere, affecting solar power generation in various parts of Europe by up to 20%. This type of dust cloud is quite common and can reduce clear sky irradiance (leading to solar power generation) by up to 20%, but fortunately, this situation will only last for a few days. According to the analysis using the Solcast API, this week's dust clouds will dissipate on Saturday, reducing the impact on areas further north and mountainous areas protected by the Alps. The low-pressure system over the Mediterranean has triggered a serious sand and dust transport event, affecting solar power generation throughout Europe for the entire week. The weak low-pressure system in the Mediterranean forms a southerly wind, which passes through the Mediterranean from Sahara Africa and enters Europe, blowing sand and dust into southern Italy and France. The high-pressure ridge from the Atlantic forms a westerly wind, blowing sand and dust from the northern Alps into southern Germany. By Saturday, the intensity of sand and dust will greatly decrease, mixing and dispersing with the upper atmosphere, thus being diluted. The impact on clear sky irradiance is very significant, with the global level of clear sky irradiance (GHI) in Marseille decreasing by more than 20% compared to the average level. In summer, it is not uncommon for Sahara dust transport to cross the Mediterranean, as the Azores high-pressure system moves northward, creating more low-pressure systems in the Mediterranean. That's why Italy, which extends to the Mediterranean, is usually more susceptible to the impact of such dust transport.
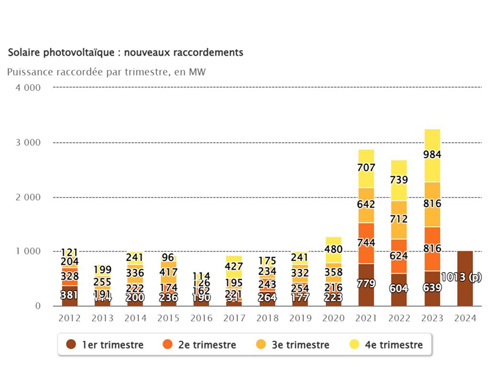
The French Ministry of Ecological Transformation reported that approximately 1013 MW of new photovoltaic power generation systems were successfully connected to the grid in France from January to March this year. In contrast, the country's installed capacity in the fourth quarter of 2023 was 984 MW, compared to an additional 639 MW in the first quarter of last year. As of the end of March 2024, France's cumulative photovoltaic installed capacity has reached 21.1 GW. Among them, major developers have deployed approximately 20.3 GW in mainland France, while the rest are distributed in Corsica and French overseas territories. At present, the total capacity of solar projects queuing up for grid connection is 27.3 GW, of which approximately 6.3 GW have already signed preliminary grid connection agreements. The new Aquitaine region, Auvergne Rh ô ne Alpes region, Provence Alpes Blue Coast region, and the Greater East region of France account for 47% of the total new installed capacity so far this year. These regions with the largest installed capacity account for over 53% of France's cumulative grid connected capacity as of the end of March.

The Philippine government has put into operation the largest solar irrigation system in the Philippines, consisting of more than 1,000 solar panels and two submersible pumps. The project, built between July 2023 and February 2024, cost 65.7 million Philippine pesos ($1.1 million) and has more than 1,000 solar panels. Its two submersible pumps can produce 739,200 watts of power, and each pump can drain 12,800 gallons (48,453 liters) per minute. Philippine President Ferdinand R. Marcos Jr. said the project is the largest solar pumped irrigation project in the Philippines to date, irrigating 350 hectares of rice fields and helping nearly 237 farmers. Isabela Province is the largest corn producing region and the second largest rice producing region in the Philippines. The project is the first in the Philippines to be built on irrigation canals, meaning there will be no less land for farmers to cultivate. President Marcos said another 152 solar water pump irrigation projects are under construction across the country, including 118 government-regulated projects. At the same time, 82 solar irrigation projects have been built and put into use since 2023.

The International Energy Agency (IEA) has released a new report saying that the world is likely to miss the target of expanding global renewable energy capacity to 11,000 GW by 2030, agreed at the 28th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP28). The report also predicts that solar power will overtake hydropower to account for the largest share of the world's installed renewable energy capacity. The IEA reports that national governments have set domestic renewable energy ambitions that exceed those of the NDC. The agency's analysis of policies, plans and estimates from nearly 150 countries shows that nearly 8,000 GW of renewable energy will be installed globally by 2030, accounting for 70% of the capacity needed to achieve the tripling target by 2030. The IEA said that in order to reach 11,000 GW, most regions and countries, including the European Union, the United States and India, "need to accelerate" the pace of deployment. Southeast Asia, the Middle East, North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa require increased deployment, according to the report. The report also notes that China's renewable energy expansion is critical to achieving the 11,000 GW target, with the country so far on track to exceed the 2030 target by 2.5 times. Since the signing of the Paris Agreement in 2015, new annual renewable energy capacity has tripled, according to the report. The IEA attributes this achievement to policy support, economies of scale and technological advances. The International Energy Agency has revealed that solar energy accounts for half of the future capacity that governments have clearly mapped out. It predicts that once countries meet their 2030 targets, the sun will overtake hydropower to become the world's largest source of installed renewable energy capacity. The report also identifies key challenges to renewable energy deployment, including long waiting times for approvals, inadequate investment in grid infrastructure, the need for rapid and efficient integration of variable renewables, and high financing costs, especially for emerging and developing economies. It calls for lower financing costs to improve the financing viability of renewable energy projects and to provide project support in the pre-development stage. In April, the International Energy Agency called for a six-fold increase in global energy storage capacity to drive the 2030 global goal.

Swiss voters have approved a new electricity regulation that makes it mandatory for large buildings to install photovoltaic systems to support the power community and encourage collective energy self-use. Some 68.72% of Swiss voted in favour of new electricity regulations to speed up the development of renewable energy. The law provides new incentives for the development of photovoltaic power generation, and new buildings with a surface of more than 300 square meters must install solar installations on the roof or external walls. States may extend this requirement to buildings with a floor area of not more than 300 square meters. Swissolar, a Swiss industry association, said in a press release: "The Ministry's electricity law lays the necessary foundation for continued growth in solar power generation - mainly located in buildings and infrastructure and delivered by highly efficient installations in winter." Solar energy will become the second pillar of Switzerland's energy supply, alongside hydropower." The new regulations also support local power communities and expand self-use groups. Distribution network operators must sell more electricity from local renewable sources to customers. According to Swissolar, Switzerland will install more than 1.5 GW of PV systems by 2023.以上翻译结果来自有道神经网络翻译(YNMT)· 通用场景

Chinese developer Eging PV Technology said it will build a 200 MW solar power station in southwestern Tajikistan. The project will be developed in four phases, with a $150 million investment in the first phase to build a solar power plant on 250 hectares of land. According to a statement from Tajikistan's Energy Ministry, the total investment in the four phases of the project will amount to $1.5 billion. Tajikistan will also lay the foundation stone for the construction of the country's first solar equipment production plant with the investment of South Korea's Global solar Wafer company. The plant is expected to cost $2 million. Construction of the plant will begin in July, with the first of four phases scheduled to be completed by March 2025. According to a statement from the presidential press Service, the initial manufacturing capacity of the plant is expected to reach 5,000 MW. Once fully operational, the plant will provide 8,000 jobs, 95 percent of which will be allocated to Tajik citizens. In October 2023, Tajikistan announced plans for 500 MW of renewable energy, including floating photovoltaic installations, and set a target of 1 GW of renewable energy generation by 2030. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Tajikistan does not have any installed PV capacity at the end of 2023.

The European Executive Agency for Climate, Infrastructure and the Environment (CINEA) has signed grant agreements with seven solar projects in Finland with a total capacity of 212.99 MW. Following the success of the EU's first cross-border solar tender last year, the EU Renewable Energy Financing Facility has invested a total of €27.5 million in these projects. These include two projects in the South Ostbotten region of western Finland, a 74.03 MW plant in an area currently used for peat production and a 33 MW plant in a peat bog. In addition, the 20-megawatt surface solar park in Loukkaanaro will be the largest solar project in northern Finland and is expected to operate for at least 30 years. Other projects funded include a 40.16 MW power plant in Poytya in southwestern Finland, a 30 MW power park in the city of Tohmajarvi in the North Karelia region of eastern Finland, and an 8 MW power park in the city of Nivala in central Finland Megawatt power plant and a 7.8-megawatt power plant in the city of Savonlinna in eastern Finland.

Ausgrid, a distributed networking provider in New South Wales, Australia, has commissioned its third battery energy storage system as part of the federal government's AU $200 million (US $132 million) Home Solar Community Battery program. Ausgrid says the 250 kW/535 kWh battery storage system installed in the Sydney suburb of North Epping will allow households without rooftop PV systems to benefit from renewable energy, while also easing pressure on the grid by absorbing excess solar power. Ausgrid CEO Marc England said the benefits of community batteries are huge, providing a flexible, scalable energy solution that benefits the local communities in which they are located and the wider energy system. "Batteries like this can maintain local power quality and voltage, enabling residents to install more solar and feed that solar energy into the grid, supporting home electrification and electric vehicle charging," he said, adding, "Batteries will also provide system-wide benefits, supporting more intermittent renewable energy generation by bridging the gap between when energy is generated and when it is needed." " England said that with the right regulatory setup, Ausgrid could provide more than 1 GW to 2 GW of storage capacity in its network, which he believes will improve the safety and reliability of the power system.

The Irish government has announced the second phase of its Small-scale Renewable Electricity Support Scheme (SRESS). The latest phase targets community and local projects, or Renewable energy communities (RECs). In addition to export-only projects under 1 MW, it also targets small and medium-sized enterprises (smes) that produce their own solar or wind power. The scheme provides guaranteed feed-in tariffs without the need for auctions. Government guidelines state that successful applicants will receive a premium on their renewable electricity market income. Electricity prices for renewable energy certificates have been set at 150 euros ($162.70) per megawatt-hour for solar projects up to 1 MW and 140 euros per megawatt-hour for projects between 1 MW and 6 MW. For smes, the electricity price for solar projects up to 1 MW is 130 euros/MWH and 120 euros/MWH for projects between 1 MW and 6 MW. The scheme sets cheaper electricity prices for wind projects. According to government guidance, electricity prices for renewable energy certificates are higher because such projects face additional hurdles in developing planning, grid connectivity and financing, and also reflect public policy preferences for community participation in renewable energy projects. The Irish Solar Energy Association welcomed the latest phase of the scheme, saying it "presents a significant opportunity for communities, local businesses and smes to drive Ireland's transition to renewable energy". The first phase of the Irish SRESS will be launched in 2023 for self-use of more than 50 kW and less than 1 MW. The third phase is expected to support all applicant categories and is currently scheduled to start in 2026. The Irish government has set a target that 80% of its energy market will come from renewables by 2030.
Categories
New Products
Tin Roof Rapid Solar Mounting System with Hanger Bolt Read More
Residential Small Solar Easy Bracket Kit for Home Balcony Read More
Automatic Single Pile Solar Tracker with 10 PV Panels Read More
Angle Adjustable Aluminum Easy Solar Panel Bracket for Garden Read More
Intelligent Single Post Dual Row Solar Tracking System Read More
5000ES Solar Off-Grid Energy Storage Inverter Supplier Read More
Multi Drive Double-Sided Single Axis Tracker System Read More
© Copyright: 2025 Xiamen Wintop New Energy Tech Co., Ltd.. All Rights Reserved.

IPv6 network supported